SEO vs. GEO: Key Differences and Science-Based Tips for 2025

For years, SEO was the go-to strategy for getting found online. If you nailed your rankings, backlinks, and keywords, you had a shot at real traffic.
But with the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs)—like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude—the rules are shifting.
Now, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is changing how content gets discovered.
Instead of competing for Google rankings, GEO focuses on getting cited in AI-generated responses.
And this isn’t just theory.
A Seer Interactive study found that websites appearing anywhere on Google’s first page had a positive correlation with being cited by AI, but backlinks and domain authority showed little to no influence.
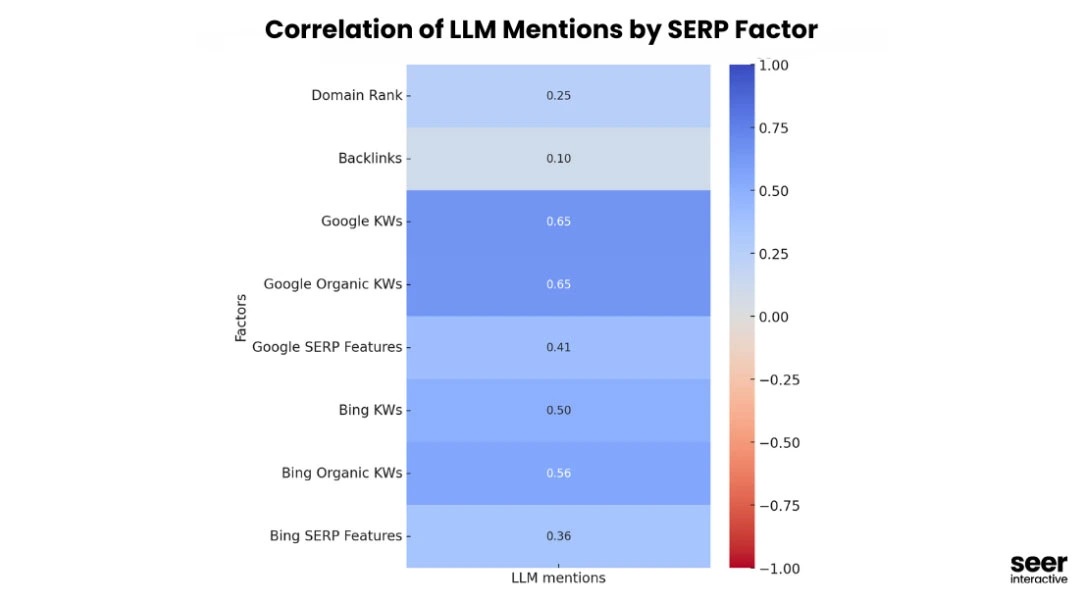
This means you don’t need to be the #1 ranked site or have the most backlinks to be referenced in AI-generated answers.
So, how exactly do SEO and GEO differ? And where do they overlap?
It all comes down to two key factors:
✅ Trustworthiness of your website (How credible your website or brand is)
✅ Content optimization (How well your content is structured for AI and search engines)
Both SEO and GEO rely on these factors, but they value them differently—and that has big implications for content creators and brands.
Let’s break it down. 🚀
TL;DR
- SEO vs. GEO: SEO is about ranking #1 for clicks; GEO is about getting cited as a trusted source in AI-generated responses (ChatGPT, Perplexity).
- Distributed Visibility: Unlike Google's "winner-takes-all" model, AI synthesizes answers from multiple sources, allowing niche sites to compete with giants.
- Trust Signals: While SEO values backlinks and Domain Authority, GEO prioritizes brand mentions, expert citations, and factual accuracy.
- Science-Backed Tactics: Adding statistics, peer-reviewed citations, and expert quotes can boost AI citations by up to 40%.
- 2026 Strategy: Focus on content structure and readability (Flesch-Kincaid grade 8-10) to help AI "snatch" information easily.
How GEO Levels the Playing Field (Without Relying on Google’s Traditional Rankings)
One of the biggest differences between SEO and GEO is who gets visibility.
SEO favors websites that already have authority—sites with years of backlinks, brand recognition, and high domain authority.
GEO, on the other hand, opens the playing field by prioritizing trustworthiness and relevance over pure ranking power.
That means new creators don’t need to fight for a top Google position to be visible in AI-driven search results.
But how exactly does this work?
Google search results are hierarchical—if you’re not in the top 3 results, you’re almost invisible.
🔹 The #1 search organic result gets 46% of all clicks (source: Advanced Web Rankings).
🔹 The #5 result gets around 4% of clicks.
🔹 Around 1% of users click on anything on page 2.
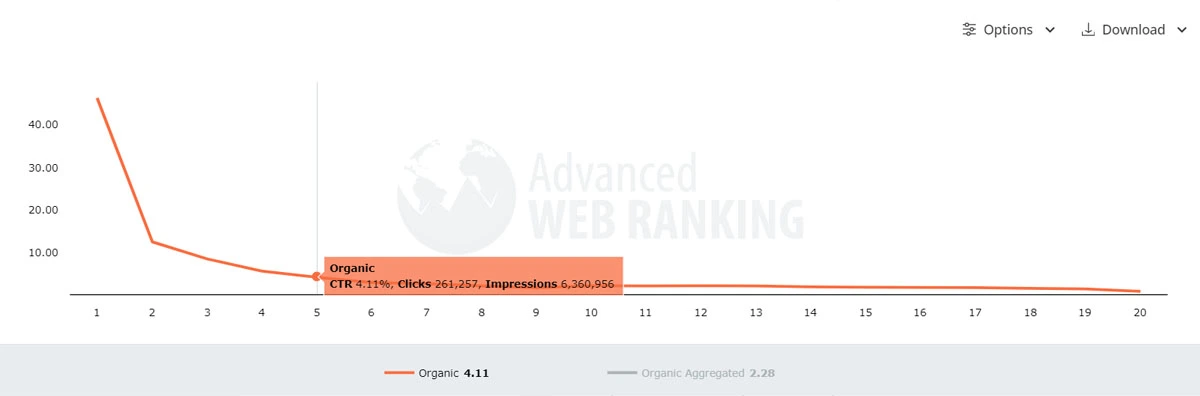
If you’re not at the top, you barely get seen at all.
And getting to the top is incredibly difficult because Google relies on ranking factors like domain authority, backlinks, and user behavior metrics—which overwhelmingly favor big brands and well-established sites.
In short, SEO is a race where the winner takes it all.
However...
GEO Spreads Visibility Across Multiple Sources
GEO doesn’t rank content the same way.
Instead of showing a list of links, AI-generated responses synthesize information from multiple sources to create a complete answer.
This changes the game because:
✅ AI doesn’t just take information from the #1 search result—it looks for multiple credible sources.
✅ Content doesn’t have to rank #1 to be included—it just needs to be valuable, structured, and well-cited.
✅ Lower-ranked or niche sites can be cited alongside high-authority domains—if they offer unique insights, statistics, or expert-backed claims.
This doesn’t mean GEO ignores trustworthiness—far from it.
Instead of relying on domain authority like SEO, GEO looks at brand mentions, citations, and verifiable sources to determine which content is worth referencing.
SEO = Authority; GEO = Trustworthiness
SEO’s ranking system is hierarchical:
🔹 The highest-ranked result gets the most visibility.
🔹 Google determines rankings based on backlinks, click-through rates, and domain authority.
GEO’s citation system is distributed:
🔹 AI pulls from multiple sources to build its response.
🔹 It doesn’t rank pages but selects the most relevant and trusted content.
🔹 Trustworthiness is measured by brand mentions, expert citations, and factual accuracy.
But wait a minute… does this mean new websites can still show up in AI search results?
Well, not so fast...
How GEO Determines Trustworthiness and Selects Sources to Reference
At the core of GEO, two key factors determine whether your content gets cited in AI search results:
- The trustworthiness of your website
- The trustworthiness and structure of the content itself
Unlike Google, which primarily ranks content based on SERP algorithms, AI-driven Generative Engines (GEs) decide what to cite based on trustworthiness signals rather than traditional SEO metrics like domain authority or backlinks.
Here’s how AI tools prioritize sources:
1. Pre-Trained Knowledge (What AI Already Knows)
🔹 AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude are trained on vast datasets, including books, research papers, and high-authority web sources (Wikipedia, government sites, academic journals).
🔹 This means that certain high-authority sources are already “trusted” even before AI tools fetch real-time data.
➡️ This means that if your content isn’t already part of an AI model’s pre-training, it needs to prove credibility through real-time sources.
2. Live Web Retrieval (How AI Fetches New Information)
When AI models fetch live data (like Perplexity AI, ChatGPT Browsing Mode, or Bing AI), they prioritize sources that have:
✅ SERP Rankings (yes, SEO still matters)
- AI often fetches from top-ranking Google results, meaning SEO and GEO still intersect.
- If your content ranks well in Google, Bing, or other search engines, AI tools are more likely to pull from it.
✅ Brand Mentions Across the Web
- If other sources frequently mention your brand, AI tools view your content as more credible.
- Example: If your website is referenced in a Forbes article, AI will likely trust your content even if your domain is new.
3. Social Proof (Reputation Beyond SEO)
GEO doesn’t just look at ranking algorithms—it considers how widely accepted and referenced a source is online.
🔹 Are other experts citing or referencing your content?
🔹 Are industry blogs, social media, or forums discussing your insights?
🔹 Does your brand name appear in multiple contexts (not just your own website)?
🚀 In other words, GEO favors sources that have established credibility—through search rankings, citations, and brand mentions.
However, new or smaller websites can still greatly benefit from GEO by simply optimizing their content, and this is where the trustworthiness and structure of the content itself comes in.
Here's how...
How Can Smaller Websites Compete with Bigger Brands in GEO (Without SEO Authority)?
A 2023 study by Aggarwal et al. looked into how content can be optimized for Generative Engines (GEs) like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini.
And they found that smaller websites can dramatically increase their AI citations—without needing high domain authority.
For example, websites ranked 5th in Google’s search results saw a 115.1% increase in AI citations just by including authoritative sources within their content—citing credible references and adding structured data.
In contrast, top-ranked websites actually saw a 30.3% decrease in visibility when relying only on traditional SEO tactics.
This means even if your site doesn’t dominate traditional SEO rankings, you can still get referenced in AI-generated responses.
So, if you're a smaller website looking to compete with industry giants, here are some proven tactics you can implement—backed by science.
1. Add Credible Citations and Data
The study "GEO: Generative Engine Optimization" (Aggarwal et al., 2023) found that adding peer-reviewed citations and data-backed claims boosted visibility by up to 40%.
📌 What do to:
- Reference studies, reports, and authoritative sources in your content (don't just link to the sources but actually mention them).
- Don’t just make claims—back them up with numbers and citations.
- Example: Instead of saying, “AI-generated content is growing fast,” say, “AI-generated content is projected to grow by 300% by 2026 (Source: XYZ Study).”
GEs prioritize content with external validation—they need to trust the information before citing it.
2. Make Your Content Clear and Easy to Read
Well-structured, easy-to-read content gets cited more often by AI models in 2026.
According to the study, improving fluency and readability led to a 15-30% increase in AI search visibility.
AI models extract and synthesize information. If your content is too complex or unstructured, it gets ignored.
📌 What to do:
- Use shorter sentences and clear subheadings to structure your content.
- Aim for a Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level of 8-10 (easy for AI to process).
- Break up dense information into bullet points and scannable sections.
3. Use Direct Quotes from Experts
AI loves direct, well-attributed quotes.
The study found that content containing expert quotations improved visibility by 30-40%.
📌 What to do:
- Quote industry leaders and authoritative figures in your niche.
- Attribute statements clearly (e.g., “According to SEO expert John Doe…”).
- Use blockquotes to highlight expert insights.
4. Combining Strategies for Maximum Impact
Want the best results? Combine multiple GEO techniques.
📌 The study found that the most effective combination was:
✅ Fluency Optimization + Statistics Addition → This outperformed any single GEO strategy by 5.5%.
Checkout this article for more actionable GEO strategies to implement in 2026.
Final Takeaway: SEO vs. GEO Ranking Factors
Even though SEO and GEO work differently in 2026, they still share some core principles. But the way they measure success? That’s where things change.
In summary these are the main takeaways...
1. Content Quality Still Matters—But It's Measured Differently
✅ SEO: Google tracks bounce rates and dwell time—if users leave too quickly, your rankings drop.
✅ GEO: AI doesn’t track visits. Instead, it looks at content trust—how often your content is cited and referenced in AI-generated responses.
📌 What this means for you:
- In SEO, engaging content keeps visitors on your page.
- In GEO, well-researched, data-backed content gets cited more often—whether or not users visit your site.
2. User Experience Is Key—But AI Models Focus on Structure, Not Speed
✅ SEO: Google penalizes slow-loading sites because it impacts user experience.
✅ GEO: AI doesn’t care how fast your page loads—but it penalizes poorly structured content that’s hard to extract information from.
📌 What this means for you:
- SEO: Optimize page speed, mobile responsiveness, and UX design.
- GEO: Focus on logical content flow, scannability, and structured formatting so AI can easily extract key insights.
3. Constant Optimization Is Required—For Both SEO and GEO
✅ SEO: Google updates its ranking algorithms constantly (like the Helpful Content Update).
✅ GEO: AI tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity tweak their citation models, shifting how they reference content.
📌 What this means for you:
- SEO strategies must evolve—what worked last year might not work today.
- GEO is the same—staying ahead means adjusting to how AI selects and synthesizes content.
🚀 Bottom Line:
SEO and GEO have similar goals—they both reward high-quality content and a good user experience.
But while SEO is about getting ranked, GEO is about getting cited.
To stay ahead, your content needs to work for both.
| Factor | SEO (Google) | GEO (AI Search & Generative Engines) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Rank high in SERPs | Be referenced in AI-generated answers |
| Key Ranking Factors | Backlinks, domain authority, CTR | Social proof, citations, SERP rankings, credibility |
| Top Results Matter? | Yes—#1 gets 27% of clicks | Yes, but AI pulls from multiple sources |
| How Trust is Determined | Domain history, link-building, CTR | External references, citations, brand mentions |
| Barrier for New Websites? | Very high—takes months/years to rank | Lower—but still requires validation |